CSS-WC Message objects¶
Module: dvbcss.protocol.wc
The WCMessage class represents a CSS-WC protocol message.
The Candidate class represents a measurement “candidate”
for use by a Wall Clock Client algorithm and is calculated from a WCMessage
that represents a Wall Clock protocol response message received from a server.
Example usage¶
Creating a request message at a Wall Clock Client:
>>> from dvbcss.protocol.wc import WCMessage
>>> import time
>>> t1 = time.time() * 1000000000
>>> msg = WCMessage(msgtype=WCMessage.TYPE_REQUEST, precision=-10, maxFreqError=256*50, originateNanos=t1, receiveNanos=0, transmitNanos=0)
>>> packedMessage = msg.pack()
>>> packedMessage
"\x00\x00\xf6\x00\x00\x002\x00TvH'3\xf5\xfc\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"
Processing a received response message at a Wall Clock Client:
>>> from dvbcss.protocol.wc import Candidate
>>> t4 = <nanoseconds-at-which-message-was-received>
>>> msg = WCMessage.unpack(receivedData)
>>> msg.msgtype
1
>>> c = Candidate(msg, t4)
>>> c.rtt
459734573
Classes¶
WCMessage¶
- class
dvbcss.protocol.wc.WCMessage(msgtype, precision, maxFreqError, originateNanos, receiveNanos, transmitNanos, originalOriginate=None)[source]¶Create object representing a CSS-WC wall clock request or response message.
Initialisation takes the following parameters:
Parameters:
- msgtype (int) – Type of message. One of:
TYPE_REQUEST,TYPE_RESPONSE,TYPE_RESPONSE_WITH_FOLLOWUPandTYPE_FOLLOWUP- precision (int) – Precision (of the server’s wall clock) encoded in log base 2 seconds between -128 and +127 inclusive.
- maxFreqError (int) – Maximum frequency error (of the server’s wall clock) in units of 1/256ths ppm.
- originateNanos (int) – Originate timevalue in integer number of nanoseconds
- receiveNanos (int) – Receive timevalue in integer number of nanoseconds
- transmitNanos (int) – Transmit timevalue in integer number of nanoseconds
- originalOriginate (
Noneor (int,int)) – Optional original encoding of the originate timevalue as (seconds, nanos). Overrides originateNanos if not None.The originalOriginate parameter, if not None, overrides the originateNanos parameter.
Convert to and from a string containing the binary encoding of this message using the
pack()method andunpack()class method.
msgtype[source]¶(read/write
int) Type of message. 0=request, 1=response, 2=response-with-followup, 3=followup
precision[source]¶(read/write
int) Precision encoded in log base 2 seconds between -128 and +127 inclusive. For example: -10 encodes a precision value of roughly 0.001 seconds.
maxFreqError[source]¶(read/write
int) Maximum frequency error in units of 1/256ths ppm. For example: 12800 encodes a max freq error of 50ppm.
originalOriginate[source]¶(read/write
Noneor (int,int)) Optional original encoding of the originate timevalue as (seconds, nanos). Overrides originateNanos when the message is packed if the value is not None.
TYPE_RESPONSE_WITH_FOLLOWUP= 2[source]¶Constant: Message type 2 “response to be followed by a follow-up response”
- classmethod
encodePrecision(precisionSecs)[source]¶Convert a precision value in seconds to the format used in these messages
pack()[source]¶Pack wall clock message into binary representation.
Returns: String containing the wall clock message in final bitstream form.
setPrecision(precisionSecs)[source]¶Set precision value given a precision represented as factions of a second
- classmethod
unpack(data)[source]¶Class method that takes a string containing a wall clock message and unpacks it to a
WCMessageobject.
Parameters: data (str) – String containing binary representation of a Wall Clock message as received from a client or server. Returns: WCMessageobject representing the wall clock message.
Candidate¶
- class
dvbcss.protocol.wc.Candidate(msg, nanosRx)[source]¶This object represents a measurement “candidate” to be fed into a Wall Clock Client’s algorithm. It is calculated from a
WCMessagereceived as a response from a Wall Clock server.Initialisation takes the following parameters:
Parameters: Pass in a received WallClockMessage that is a response and this will represent the candidate data derived from that request-response interaction.
Populates properties of this objects with the candidate information.
t1,t2,t3andt4represent the times of message sending and receiving as shown below: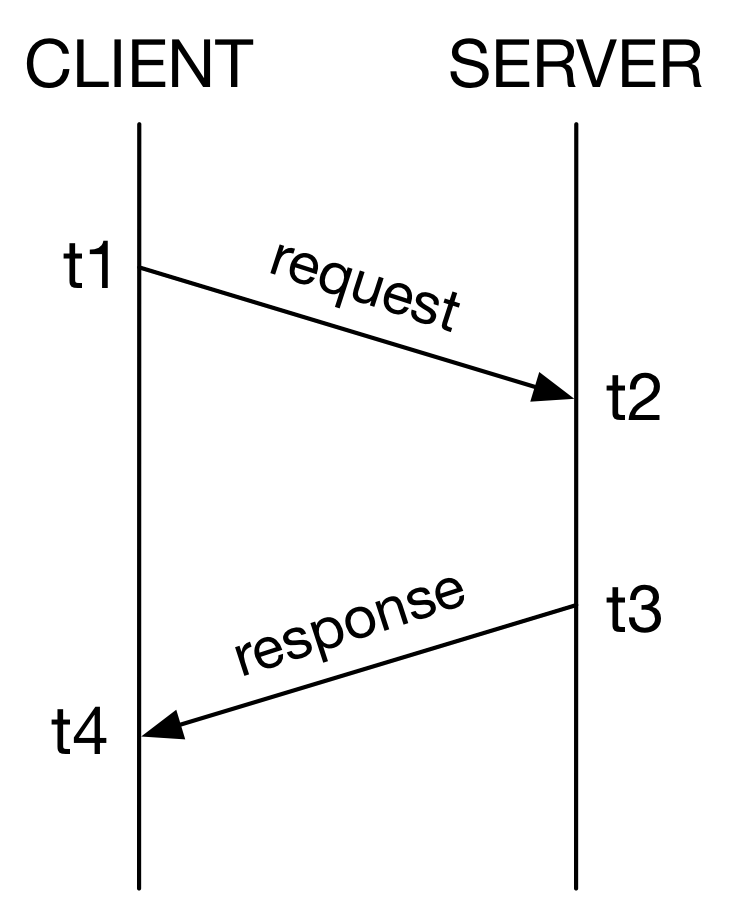
It also calculates and provides, as properties, the round-trip time (
rtt) and clock offset estimate (offset) based on this measurement.By default the data is preserved in nanoseconds. However you may use the
toTicks()method to create a new version of the Candidate object using units of ticks matching aclockobject you provide.The exceptions are precision which is measured in seconds, and maximum frequency error which is measured in ppm
t1= msg.originateNanos[source]¶(read only) The time “t1” at which the request was sent in the request-response measurement (nanoseconds, or clock ticks)
t2= msg.receiveNanos[source]¶(read only) The time “t2” at which the request was received in the request-response measurement (nanoseconds, or clock ticks)
t3= msg.transmitNanos[source]¶(read only) The time “t3” at which the response was sent in the request-response measurement (nanoseconds, or clock ticks)
t4= nanosRx[source]¶(read only) The time “t4” at which the response was received in the request-response measurement (nanoseconds, or clock ticks)
offset= ((t3+t2)-(t4+t1))/2[source]¶(read only) Server<->client clock offset (nanoseconds, or clock ticks)
isNanos= True[source]¶(read only
bool) True if this candidate object is in units of nanoseconds for t1, t2, t3, t4, offset and rtt
precision= msg.getPrecision()[source]¶(read only) The precision reported by the server in its response (units of factions of a second)
maxFreqError= msg.getMaxFreqError()[source]¶(read only) The maximum frequency error reported by the server in its response (units of ppm)
msg= WCMessage[source]¶(read only
WCMessage) The response message from which this candidate was derived
toTicks(clock)[source]¶Returns a new Candidate object the same as this one but whose measurements have been converted to match the timescale of a clock.
t1, t2, t3, t4, rtt and offset of the returned object are converted to units of ticks matching the clock. But precision and maxFreqError remain unchanged.
Parameters: clock (dvbcss.clock) – Clock whose nanosToTicks()function will be used to create the new candidate objectReturns: a copy of this candidate where the units have been converted to ‘ticks’ according to the tick rate of the supplied clock.